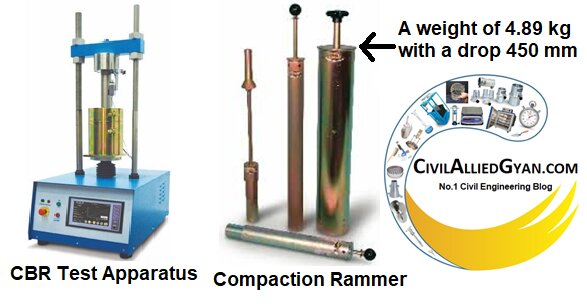
California Bearing Ratio-CBR Test Apparatus, Single Speed VSLIC - 5TON
short info
Vertex CBR Test Apparatus unit is supplied with motorized load frame having single rate of strain of 1.25 mm/m.
Standard
Model
Origin
Make/ OEM
short info
Vertex CBR Test Apparatus unit is supplied with motorized load frame having single rate of strain of 1.25 mm/m.
Standard
Model
Origin
Make/ OEM
The California Bearing Ratio Test (CBR Test) is a penetration test developed by California State Highway Department (U.S.A.) for evaluating the bearing capacity of sub grade soil for design of flexible pavement.
Tests are carried out on natural or compacted soils in water soaked or un-soaked conditions and the results so obtained are compared with the curves of standard test to have an idea of the soil strength of the sub grade soil.
Laboratory CBR Apparatus meets the essential requirements of IS:2720 (Part XVI) with the mould as per of IS:9669. The field CBR Apparatus meets the requirements of IS:2720 (Part XXXI).
The apparatus consists of :-
Suitable for a power supply of 220v, 50 Hz, single phase.
The apparatus consists of :-
The California Bearing Ratio Test (CBR Test) is a penetration test developed by California State Highway Department (U.S.A.) for evaluating the bearing capacity of sub grade soil for design of flexible pavement.
Tests are carried out on natural or compacted soils in water soaked or un-soaked conditions and the results so obtained are compared with the curves of standard test to have an idea of the soil strength of the sub grade soil.
Laboratory CBR Apparatus meets the essential requirements of IS:2720 (Part XVI) with the mould as per of IS:9669. The field CBR Apparatus meets the requirements of IS:2720 (Part XXXI).
The apparatus consists of :-

What is California Bearing Ratio (CBR) of Soil?
California Bearing Ratio (CBR) of soil is the ratio expressed in percentage of force per unit area required to penetrate a soil mass with a standard circular plunger of 50 mm diameter at the rate of 1.25 mm/min to that required for corresponding penetration in a standard material. The ratio is usually determined for penetration of 2.5 mm and 5 mm. When the ratio at 5 mm is consistently higher than that at 2.5 mm, the ratio at 5 mm is used.
The following table gives the standard loads adopted for different penetrations for the standard material with a CBR value of 100%.
| Penetration of Plunger | Standard Load |
| 2.5 mm | 1370 kg |
| 5.0 mm | 2055 kg |
Note:- For Railway Formation purpose, the test is performed on remoulded specimens which are compacted dynamically.
What is California Bearing Ratio Test (CBR Test) of Soil?
The California Bearing Ratio Test (CBR Test) of soil is a penetration test developed by California State Highway Department (U.S.A.). This test is used for evaluating the bearing capacity of sub grade soil for design of flexible pavement.
IS Code for California Bearing Ratio (CBR) Test of Soil:-
IS: 2720 (Part 16): 1987; Methods of test for soils: Determination of California Bearing Ratio (second revision) of soil.
Apparatus Required for California Bearing Ratio (CBR) Test of Soil:-
| Apparatus | Specification |
| CBR Moulds | With Base Plate, Stay Rod and Wing Nut |
| Cylindrical mould | Inside diameter 150 mm and height 175 mm with a detachable perforated base plate of 235 mm diameter and 10mm thickness. Net capacity will be 2250 ml; conforming to IS-9669: 1980 |
| Collar | A detachable extension collar of 60 mm height |
| Spacer Disc | 148 mm in diameter and 47.7 mm in height along with handle |
| Metal Rammer | Weight 4.89 kg with a drop 450 mm; for compaction |
| Expansion Measuring Apparatus | The adjustable stem with perforated plates and tripod |
| Weights | One annular metal weight and several slotted weights weighing 2.5 kg each, 147 mm in dia., with a central hole 53 mm in dia. |
| Loading Machine | With a capacity of at least 5000kg and equipped with a movable head or base which enables the plunger into penetrate into the specimen at a deformation rate of 1.25 mm/min. |
| Penetration Plunger | Metal penetration piston 50 mm diameter and minimum of 100 mm in length (conforming to IS: 9669-1980) |
| Dial Gauges | Two dial gauges sensitive to 0.01 mm |
| Sieves | 47.5 mm and 19 mm IS Sieves |
| Other apparatus
Mixing bowl, scales, straightedge, drying oven, filter paper, soaking tank or pan, dishes and calibrated measuring jar |
|
Procedure for California Bearing Ratio Test (CBR Test) of Soil:-
The CBR test of soil may be performed on undisturbed specimens or remoulded specimens which may be compacted either statically or dynamically.
Note: The static method of compaction gives the required density but requires considerable pressure and there is a possibility of the actual density varying with depth though the average density may be the one desired.
Undisturbed Specimen: Undisturbed specimen will be obtained by fitting to the mould, the steel cutting edge of 150 mm internal diameter and pushing the mould as gently as possible into the ground and digging away the soil as the mould is pushed in. When the mould is sufficiently full of soil, it will be removed by under digging, the top and bottom surface are then carefully trimmed flat so as to give the required length of specimen ready for testing. The density of the soil will be determined.
Remoulded Specimens: The dry density for a remoulding will be either the field density or the value of the maximum dry density estimated by the compaction tests.
Note: For Railway Formation, dry density is estimated by heavy compaction test as per IS: 2720: Part-8: 1983.
The water content used for compaction should be the optimum water content or the field moisture as the case may be.
Soil Sample: The test material (i.e. soil) used in the remoulded specimen should pass 19 mm IS sieve and retained on 4.75 mm IS sieve.
Statically Compacted Specimens: The mass of the wet soil at the required water content to give the desired density when occupying the standard specimen volume in the mould will be calculated. A batch of soil will be thoroughly mixed with water to give the required water content. The correct mass of the moist soils will be placed in the mould and compaction obtained by pressing in the displacer disc, a filter paper being placed between the disc and the soil.
Dynamically Compacted Specimens: For dynamic compaction, a representative sample of the soil weighing approximately 4.5 kg or more for fine-grained soil and 5.5 kg or more for granular soil will be taken and mixed thoroughly with water. If the soil is to be compacted to the maximum dry density at the optimum moisture content, the exact mass of the soil required will be taken and the necessary quantity of water added so that the water content of the soil sample is equal to the determined optimum moisture content.
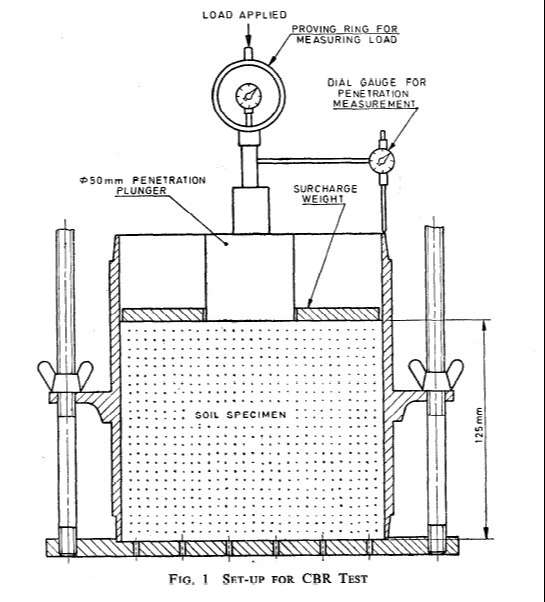
Next steps:-
Observations and Recording:-
Recordings during CBR Test
| Penetration (in mm) | Applied Load (in kg) |
| 0.50 | |
| 1.00 | |
| 1.50 | |
| 2.00 | |
| 2.50 | |
| 4.00 | |
| 5.00 | |
| 7.50 | |
| 10.00 | |
| 12.50 |
Calculations:-
Formula for California Bearing Ratio Test (CBR Test) of soil:-
a) 
Where,
dr = final dial gauge reading in mm,
ds = initial dial gauge reading in mm and
h = initial height of the specimen in mm.
b) 
Where,
PT = corrected unit (or total) test load corresponding to the chosen penetration from the load penetration curve, and
Ps = unit (or total) standard load for the same depth of penetration as for PT taken.
Report:-
The results of the California Bearing Ratio (CBR) test of soil are presented as the CBR value and the expansion ratio.
CBR of specimen at 2.5 mm penetration = …………
CBR of specimen at 5.0 mm penetration = …………
Note:- The CBR values are usually calculated for penetration of 2.5 mm and 5 mm. Generally the CBR value at 2.5 mm will be greater than at 5 mm and in such a case/the former will be taken as CBR for design purpose. If CBR for 5 mm exceeds that for 2.5 mm, the test should be repeated. If identical results follow, the CBR corresponding to 5 mm penetration should be taken for design.
The load penetration curve will be plotted (see below Fig.). This curve is usually convex upwards although the initial portion of the curve may be convex downwards due to surface irregularities. A correction will then be applied by drawing a tangent to the point of greatest slope and then transposing the axis of the load so that zero penetration is taken as the point where the tangent cuts the axis of penetration. The corrected load-penetration curve would then consist of the tangent from the new origin to the point of tangency on the re-sited curve and then the curve itself, as illustrated in below Fig.
image
Graph between Load versus Penetration.
If the initial portion of the curve is concave upwards, apply correction by drawing a tangent to the curve at the point of greatest slope and shift the origin. Find and record the correct load reading corresponding to each penetration.
Excellent machine! Accurate readings and very sturdy build. The installation team was professional and the after-sales support has been great. Highly recommend for any lab or industrial use.
KALI
Excellent machine! Accurate readings and very sturdy build … Highly recommend for any lab or industrial use.
Ratnesh
very good at Response and user friendly machines
POOJA
With the highly efficient and accurate Servo Universal Testing Machine by Vertex, Now I can test the TMT Bar great accuracy. With the help of this instrument,
Amjad Ali
The automatic blain air of flowing sample has an amazing accuracy and is simply easy to use. Our team of operators have been using it for more than 7 months now and have submitted zero complaints.
Faruq Ali
I recently purchased a Servo Compression Automatic Compressive Machine 3000kN from Vertex and I couldn’t be more pleased. The instrument is of high-quality and helps to accurately measure the strain distribution in the preforms. It is easy to use and produces reliable test results.
Ritesh
